Researchers: Huib Mansvelder (lead), Roger Adan, Sabine Spijker, Ingo Willuhn, Michel van den Oever, Priyanka Rao-Ruiz, Sophie van der Sluis, Frank Meye.
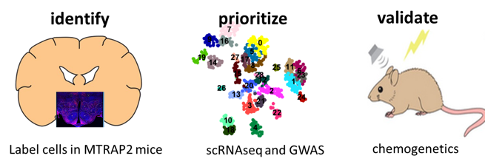
The cross-sections between results of genetic association studies, brain-wide single cell transcriptomics and connectomics have identified cell types that are potentially associated with brain disorders, such as substance abuse, depression and eating disorders. The aim of WP4 is to understand how neural circuits in which the verified cell types act, are involved in brain disorders. Such understanding is crucial for designing projects to verify novel treatment strategies targeting these cell types (WP5). Moreover, in WP4, we aim to determine whether co-morbid aspects of these disorders are generated by common circuitry.
We use translational animal models to record and manipulate the activity of genetically targeted brain-cell populations and the circuits they are embedded in. Recent developments in cell-type specific intervention integrating genetic approaches and opto- and chemo-genetic techniques enable targeting of individual neurons with genetic specificity based on projection profile. This strategy is combined with high-resolution single-cell activity recordings with implantable fibers and miniaturized microscopes (miniscope) and well-validated behavioral tests, to establish causal involvement of networks of specific subtypes of neurons in brain disorders.
In WP3, we will identify the circuitry through which disorder-specific neurons and their distal targets act, whereas in WP4, we will functionally characterize these neurons (identified in WP1 and WP2) and their specific connections in animal models of brain disorders. The long-term ambition of WP4 is to determine how cells involved in brain disorders need to be targeted in patients suffering from these disorders, in order to provide information on behavioral consequences. Outcomes of WP4, e.g. new animal models of behavior, unraveled neural circuits implicated in disease (symptoms), genetic targeting strategies including gene therapy, will be transferred to WP5 for dissemination.